Detailed Description
Threads related APIs and services.
Operation mode
A thread is an abstraction of an independent instructions flow. In ChibiOS/RT a thread is represented by a "C" function owning a processor context, state informations and a dedicated stack area. In this scenario static variables are shared among all threads while automatic variables are local to the thread.
Operations defined for threads:
- Create, a thread is started on the specified thread function. This operation is available in multiple variants, both static and dynamic.
- Exit, a thread terminates by returning from its top level function or invoking a specific API, the thread can return a value that can be retrieved by other threads.
- Wait, a thread waits for the termination of another thread and retrieves its return value.
- Resume, a thread created in suspended state is started.
- Sleep, the execution of a thread is suspended for the specified amount of time or the specified future absolute time is reached.
- SetPriority, a thread changes its own priority level.
- Yield, a thread voluntarily renounces to its time slot.

Threads queues | |
| #define | __THREADS_QUEUE_DATA(name) |
| Data part of a static threads queue object initializer. | |
| #define | THREADS_QUEUE_DECL(name) |
| Static threads queue object initializer. | |
Working Areas | |
| #define | THD_WORKING_AREA_SIZE(n) |
| Calculates the total Working Area size. | |
| #define | THD_WORKING_AREA(s, n) |
| Static working area allocation. | |
| #define | THD_WORKING_AREA_BASE(s) |
| Base of a working area casted to the correct type. | |
| #define | THD_WORKING_AREA_END(s) |
| End of a working area casted to the correct type. | |
Threads abstraction macros | |
| #define | THD_FUNCTION(tname, arg) |
| Thread declaration macro. | |
Threads initializers | |
| #define | THD_DESCRIPTOR(name, wbase, wend, prio, funcp, arg) |
| Thread descriptor initializer with no affinity. | |
| #define | THD_DESCRIPTOR_AFFINITY(name, wbase, wend, prio, funcp, arg, oip) |
| Thread descriptor initializer with no affinity. | |
Macro Functions | |
| #define | chThdSleepSeconds(sec) |
| Delays the invoking thread for the specified number of seconds. | |
| #define | chThdSleepMilliseconds(msec) |
| Delays the invoking thread for the specified number of milliseconds. | |
| #define | chThdSleepMicroseconds(usec) |
| Delays the invoking thread for the specified number of microseconds. | |
Data Structures | |
| struct | thread_descriptor_t |
| Type of a thread descriptor. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef void(* | tfunc_t) (void *p) |
| Thread function. | |
Functions | |
| thread_t * | __thd_object_init (os_instance_t *oip, thread_t *tp, const char *name, tprio_t prio) |
| Initializes a thread structure. | |
| void | __thd_stackfill (uint8_t *startp, uint8_t *endp) |
| Stack fill utility. | |
| thread_t * | chThdCreateSuspendedI (const thread_descriptor_t *tdp) |
| Creates a new thread. | |
| thread_t * | chThdCreateSuspended (const thread_descriptor_t *tdp) |
| Creates a new thread. | |
| thread_t * | chThdCreateI (const thread_descriptor_t *tdp) |
| Creates a new thread. | |
| thread_t * | chThdCreate (const thread_descriptor_t *tdp) |
| Creates a new thread. | |
| thread_t * | chThdCreateStatic (void *wsp, size_t size, tprio_t prio, tfunc_t pf, void *arg) |
| Creates a new thread. | |
| thread_t * | chThdStart (thread_t *tp) |
Starts a thread created with chThdCreateSuspended(). | |
| thread_t * | chThdAddRef (thread_t *tp) |
| Adds a reference to a thread object. | |
| void | chThdRelease (thread_t *tp) |
| Releases a reference to a thread object. | |
| void | chThdExit (msg_t msg) |
| Terminates the current thread. | |
| void | chThdExitS (msg_t msg) |
| Terminates the current thread. | |
| msg_t | chThdWait (thread_t *tp) |
| Blocks the execution of the invoking thread until the specified thread terminates then the exit code is returned. | |
| tprio_t | chThdSetPriority (tprio_t newprio) |
| Changes the running thread priority level then reschedules if necessary. | |
| void | chThdTerminate (thread_t *tp) |
| Requests a thread termination. | |
| void | chThdSleep (sysinterval_t time) |
| Suspends the invoking thread for the specified time. | |
| void | chThdSleepUntil (systime_t time) |
| Suspends the invoking thread until the system time arrives to the specified value. | |
| systime_t | chThdSleepUntilWindowed (systime_t prev, systime_t next) |
| Suspends the invoking thread until the system time arrives to the specified value. | |
| void | chThdYield (void) |
| Yields the time slot. | |
| msg_t | chThdSuspendS (thread_reference_t *trp) |
| Sends the current thread sleeping and sets a reference variable. | |
| msg_t | chThdSuspendTimeoutS (thread_reference_t *trp, sysinterval_t timeout) |
| Sends the current thread sleeping and sets a reference variable. | |
| void | chThdResumeI (thread_reference_t *trp, msg_t msg) |
| Wakes up a thread waiting on a thread reference object. | |
| void | chThdResumeS (thread_reference_t *trp, msg_t msg) |
| Wakes up a thread waiting on a thread reference object. | |
| void | chThdResume (thread_reference_t *trp, msg_t msg) |
| Wakes up a thread waiting on a thread reference object. | |
| msg_t | chThdEnqueueTimeoutS (threads_queue_t *tqp, sysinterval_t timeout) |
| Enqueues the caller thread on a threads queue object. | |
| void | chThdDequeueNextI (threads_queue_t *tqp, msg_t msg) |
| Dequeues and wakes up one thread from the threads queue object, if any. | |
| void | chThdDequeueAllI (threads_queue_t *tqp, msg_t msg) |
| Dequeues and wakes up all threads from the threads queue object. | |
| static thread_t * | chThdGetSelfX (void) |
Returns a pointer to the current thread_t. | |
| static tprio_t | chThdGetPriorityX (void) |
| Returns the current thread priority. | |
| static systime_t | chThdGetTicksX (thread_t *tp) |
| Returns the number of ticks consumed by the specified thread. | |
| static stkalign_t * | chThdGetWorkingAreaX (thread_t *tp) |
| Returns the working area base of the specified thread. | |
| static bool | chThdTerminatedX (thread_t *tp) |
Verifies if the specified thread is in the CH_STATE_FINAL state. | |
| static bool | chThdShouldTerminateX (void) |
| Verifies if the current thread has a termination request pending. | |
| static thread_t * | chThdStartI (thread_t *tp) |
Resumes a thread created with chThdCreateI(). | |
| static void | chThdSleepS (sysinterval_t ticks) |
| Suspends the invoking thread for the specified number of ticks. | |
| static void | chThdQueueObjectInit (threads_queue_t *tqp) |
| Initializes a threads queue object. | |
| static bool | chThdQueueIsEmptyI (threads_queue_t *tqp) |
Evaluates to true if the specified queue is empty. | |
| static void | chThdDoDequeueNextI (threads_queue_t *tqp, msg_t msg) |
| Dequeues and wakes up one thread from the threads queue object. | |
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ __THREADS_QUEUE_DATA
| #define __THREADS_QUEUE_DATA | ( | name | ) |
Data part of a static threads queue object initializer.
This macro should be used when statically initializing a threads queue that is part of a bigger structure.
- Parameters
-
[in] name the name of the threads queue variable
Definition at line 105 of file chthreads.h.
◆ THREADS_QUEUE_DECL
| #define THREADS_QUEUE_DECL | ( | name | ) |
Static threads queue object initializer.
Statically initialized threads queues require no explicit initialization using queue_init().
- Parameters
-
[in] name the name of the threads queue variable
Definition at line 114 of file chthreads.h.
◆ THD_WORKING_AREA_SIZE
| #define THD_WORKING_AREA_SIZE | ( | n | ) |
Calculates the total Working Area size.
- Parameters
-
[in] n the stack size to be assigned to the thread
- Returns
- The total used memory in bytes.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 130 of file chthreads.h.
Referenced by chThdCreateStatic(), and chThdCreateSuspendedI().
◆ THD_WORKING_AREA
| #define THD_WORKING_AREA | ( | s, | |
| n ) |
Static working area allocation.
This macro is used to allocate a static thread working area aligned as both position and size.
- Parameters
-
[in] s the name to be assigned to the stack array [in] n the stack size to be assigned to the thread
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 143 of file chthreads.h.
◆ THD_WORKING_AREA_BASE
| #define THD_WORKING_AREA_BASE | ( | s | ) |
Base of a working area casted to the correct type.
- Parameters
-
[in] s name of the working area
Definition at line 150 of file chthreads.h.
◆ THD_WORKING_AREA_END
| #define THD_WORKING_AREA_END | ( | s | ) |
End of a working area casted to the correct type.
- Parameters
-
[in] s name of the working area
Definition at line 157 of file chthreads.h.
◆ THD_FUNCTION
| #define THD_FUNCTION | ( | tname, | |
| arg ) |
Thread declaration macro.
- Note
- Thread declarations should be performed using this macro because the port layer could define optimizations for thread functions.
Definition at line 170 of file chthreads.h.
◆ THD_DESCRIPTOR
| #define THD_DESCRIPTOR | ( | name, | |
| wbase, | |||
| wend, | |||
| prio, | |||
| funcp, | |||
| arg ) |
Thread descriptor initializer with no affinity.
- Parameters
-
[in] name thread name [in] wbase pointer to the working area base [in] wend pointer to the working area end [in] prio thread priority [in] funcp thread function pointer [in] arg thread argument
Definition at line 188 of file chthreads.h.
Referenced by chThdCreateFromHeap(), and chThdCreateFromMemoryPool().
◆ THD_DESCRIPTOR_AFFINITY
| #define THD_DESCRIPTOR_AFFINITY | ( | name, | |
| wbase, | |||
| wend, | |||
| prio, | |||
| funcp, | |||
| arg, | |||
| oip ) |
Thread descriptor initializer with no affinity.
- Parameters
-
[in] name thread name [in] wbase pointer to the working area base [in] wend pointer to the working area end [in] prio thread priority [in] funcp thread function pointer [in] arg thread argument [in] oip instance affinity
Definition at line 219 of file chthreads.h.
◆ chThdSleepSeconds
| #define chThdSleepSeconds | ( | sec | ) |
Delays the invoking thread for the specified number of seconds.
- Note
- The specified time is rounded up to a value allowed by the real system tick clock.
- The maximum specifiable value is implementation dependent.
- Use of this macro for large values is not secure because integer overflows, make sure your value can be correctly converted.
- Parameters
-
[in] sec time in seconds, must be different from zero
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 247 of file chthreads.h.
◆ chThdSleepMilliseconds
| #define chThdSleepMilliseconds | ( | msec | ) |
Delays the invoking thread for the specified number of milliseconds.
- Note
- The specified time is rounded up to a value allowed by the real system tick clock.
- The maximum specifiable value is implementation dependent.
- Use of this macro for large values is not secure because integer overflows, make sure your value can be correctly converted.
- Parameters
-
[in] msec time in milliseconds, must be different from zero
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 263 of file chthreads.h.
Referenced by start_p_measurement(), and start_t_measurement().
◆ chThdSleepMicroseconds
| #define chThdSleepMicroseconds | ( | usec | ) |
Delays the invoking thread for the specified number of microseconds.
- Note
- The specified time is rounded up to a value allowed by the real system tick clock.
- The maximum specifiable value is implementation dependent.
- Use of this macro for large values is not secure because integer overflows, make sure your value can be correctly converted.
- Parameters
-
[in] usec time in microseconds, must be different from zero
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 279 of file chthreads.h.
Typedef Documentation
◆ tfunc_t
| typedef void(* tfunc_t) (void *p) |
Thread function.
Definition at line 52 of file chthreads.h.
Function Documentation
◆ __thd_object_init()
| thread_t * __thd_object_init | ( | os_instance_t * | oip, |
| thread_t * | tp, | ||
| const char * | name, | ||
| tprio_t | prio ) |
Initializes a thread structure.
- Note
- This is an internal functions, do not use it in application code.
- Parameters
-
[in] oip pointer to the OS instance [in] tp pointer to the thread [in] name thread name [in] prio the priority level for the new thread
- Returns
- The same thread pointer passed as parameter.
- Function Class:
- Not an API, this function is for internal use only.
Definition at line 89 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_CFG_THREAD_INIT_HOOK, CH_CFG_TIME_QUANTUM, CH_FLAG_MODE_STATIC, ch_list_init(), ch_queue_init(), CH_STATE_WTSTART, chTMObjectInit(), ch_thread::epending, ch_thread::flags, ch_thread::hdr, ch_thread::msgqueue, ch_thread::mtxlist, ch_thread::name, ch_thread::owner, ch_thread::pqueue, ch_priority_queue::prio, ch_thread::realprio, ch_thread::refs, REG_INSERT, ch_thread::state, ch_thread::stats, ch_thread::ticks, ch_thread::time, and ch_thread::waiting.
Referenced by chInstanceObjectInit(), chThdCreateStatic(), and chThdCreateSuspendedI().
◆ __thd_stackfill()
| void __thd_stackfill | ( | uint8_t * | startp, |
| uint8_t * | endp ) |
Stack fill utility.
- Parameters
-
[in] startp first address to fill [in] endp last address to fill +1
- Function Class:
- Not an API, this function is for internal use only.
Definition at line 140 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_DBG_STACK_FILL_VALUE, and likely.
Referenced by chInstanceObjectInit(), chThdCreate(), chThdCreateFromHeap(), chThdCreateFromMemoryPool(), chThdCreateStatic(), and chThdCreateSuspended().
◆ chThdCreateSuspendedI()
| thread_t * chThdCreateSuspendedI | ( | const thread_descriptor_t * | tdp | ) |
Creates a new thread.
The new thread is initialized but not inserted in the ready list, the initial state is CH_STATE_WTSTART.
- Postcondition
- The created thread has a reference counter set to one, it is caller responsibility to call
chThdRelease()orchThdWait()in order to release the reference. The thread persists in the registry until its reference counter reaches zero. -
The initialized thread can be subsequently started by invoking
chThdStart(),chThdStartI()orchSchWakeupS()depending on the execution context.
- Note
- A thread can terminate by calling
chThdExit()or by simply returning from its main function. -
Threads created using this function do not obey to the
CH_DBG_FILL_THREADSdebug option because it would keep the kernel locked for too much time.
- Parameters
-
[in] tdp pointer to the thread descriptor
- Returns
- The pointer to the
thread_tstructure allocated for the thread into the working space area.
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 171 of file chthreads.c.
References __thd_object_init(), thread_descriptor_t::arg, chDbgCheck, chDbgCheckClassI, currcore, thread_descriptor_t::funcp, HIGHPRIO, thread_descriptor_t::instance, MEM_ALIGN_NEXT, MEM_IS_ALIGNED, thread_descriptor_t::name, PORT_SETUP_CONTEXT, PORT_STACK_ALIGN, PORT_WORKING_AREA_ALIGN, thread_descriptor_t::prio, THD_WORKING_AREA_SIZE, threadref, ch_thread::wabase, thread_descriptor_t::wbase, and thread_descriptor_t::wend.
Referenced by chThdCreate(), chThdCreateFromHeap(), chThdCreateFromMemoryPool(), chThdCreateI(), and chThdCreateSuspended().
◆ chThdCreateSuspended()
| thread_t * chThdCreateSuspended | ( | const thread_descriptor_t * | tdp | ) |
Creates a new thread.
The new thread is initialized but not inserted in the ready list, the initial state is CH_STATE_WTSTART.
- Postcondition
- The created thread has a reference counter set to one, it is caller responsibility to call
chThdRelease()orchThdWait()in order to release the reference. The thread persists in the registry until its reference counter reaches zero. -
The initialized thread can be subsequently started by invoking
chThdStart(),chThdStartI()orchSchWakeupS()depending on the execution context.
- Note
- A thread can terminate by calling
chThdExit()or by simply returning from its main function.
- Parameters
-
[in] tdp pointer to the thread descriptor
- Returns
- The pointer to the
thread_tstructure allocated for the thread into the working space area.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 226 of file chthreads.c.
References __thd_stackfill(), chDbgAssert, chRegFindThreadByWorkingArea(), chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdCreateSuspendedI(), thread_descriptor_t::wbase, and thread_descriptor_t::wend.

◆ chThdCreateI()
| thread_t * chThdCreateI | ( | const thread_descriptor_t * | tdp | ) |
Creates a new thread.
The new thread is initialized and make ready to execute.
- Postcondition
- The created thread has a reference counter set to one, it is caller responsibility to call
chThdRelease()orchThdWait()in order to release the reference. The thread persists in the registry until its reference counter reaches zero.
- Note
- A thread can terminate by calling
chThdExit()or by simply returning from its main function. -
Threads created using this function do not obey to the
CH_DBG_FILL_THREADSdebug option because it would keep the kernel locked for too much time.
- Parameters
-
[in] tdp pointer to the thread descriptor
- Returns
- The pointer to the
thread_tstructure allocated for the thread into the working space area.
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 264 of file chthreads.c.
References chSchReadyI(), and chThdCreateSuspendedI().
Referenced by chInstanceObjectInit().
◆ chThdCreate()
| thread_t * chThdCreate | ( | const thread_descriptor_t * | tdp | ) |
Creates a new thread.
The new thread is initialized and make ready to execute.
- Postcondition
- The created thread has a reference counter set to one, it is caller responsibility to call
chThdRelease()orchThdWait()in order to release the reference. The thread persists in the registry until its reference counter reaches zero.
- Note
- A thread can terminate by calling
chThdExit()or by simply returning from its main function.
- Parameters
-
[in] tdp pointer to the thread descriptor
- Returns
- The pointer to the
thread_tstructure allocated for the thread into the working space area.
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 285 of file chthreads.c.
References __thd_stackfill(), chDbgAssert, chRegFindThreadByWorkingArea(), chSchWakeupS, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdCreateSuspendedI(), MSG_OK, thread_descriptor_t::wbase, and thread_descriptor_t::wend.
◆ chThdCreateStatic()
Creates a new thread.
- Postcondition
- The created thread has a reference counter set to one, it is caller responsibility to call
chThdRelease()orchThdWait()in order to release the reference. The thread persists in the registry until its reference counter reaches zero.
- Note
- A thread can terminate by calling
chThdExit()or by simply returning from its main function.
- Parameters
-
[out] wsp pointer to a working area dedicated to the thread stack [in] size size of the working area [in] prio priority level for the new thread [in] pf thread function [in] arg an argument passed to the thread function. It can be NULL.
- Returns
- The pointer to the
thread_tstructure allocated for the thread into the working space area.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 326 of file chthreads.c.
References __thd_object_init(), __thd_stackfill(), chDbgAssert, chDbgCheck, chRegFindThreadByWorkingArea(), chSchWakeupS, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, currcore, HIGHPRIO, MEM_ALIGN_NEXT, MEM_IS_ALIGNED, MSG_OK, PORT_SETUP_CONTEXT, PORT_STACK_ALIGN, PORT_WORKING_AREA_ALIGN, THD_WORKING_AREA_SIZE, threadref, and ch_thread::wabase.
◆ chThdStart()
Starts a thread created with chThdCreateSuspended().
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- Thread to be started.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 379 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_STATE_WTSTART, chDbgAssert, chSchWakeupS, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, MSG_OK, and ch_thread::state.
◆ chThdAddRef()
Adds a reference to a thread object.
- Precondition
- The configuration option
CH_CFG_USE_REGISTRYmust be enabled in order to use this function.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The same thread pointer passed as parameter representing the new reference.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 401 of file chthreads.c.
References chDbgAssert, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, and ch_thread::refs.
◆ chThdRelease()
| void chThdRelease | ( | thread_t * | tp | ) |
Releases a reference to a thread object.
If the references counter reaches zero and the thread is in the CH_STATE_FINAL state then the thread's memory is returned to the proper allocator and the thread is removed from the registry.
Threads whose counter reaches zero and are still active become "detached". Detached static threads will be removed from the registry on termination. Detached non-static threads can only be removed by performing a registry scan operation.
- Precondition
- The configuration option
CH_CFG_USE_REGISTRYmust be enabled in order to use this function.
- Note
- Static threads are not affected, only removed from the registry.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 429 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_FLAG_MODE_HEAP, CH_FLAG_MODE_MASK, CH_FLAG_MODE_MPOOL, CH_STATE_FINAL, chDbgAssert, chHeapFree(), chPoolFree(), chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdGetWorkingAreaX(), ch_thread::flags, ch_thread::mpool, ch_thread::refs, REG_REMOVE, and ch_thread::state.
Referenced by chRegNextThread(), and chThdWait().
◆ chThdExit()
| void chThdExit | ( | msg_t | msg | ) |
Terminates the current thread.
The thread goes in the CH_STATE_FINAL state holding the specified exit status code, other threads can retrieve the exit status code by invoking the function chThdWait().
- Postcondition
- Eventual code after this function will never be executed, this function never returns. The compiler has no way to know this so do not assume that the compiler would remove the dead code.
- Parameters
-
[in] msg thread exit code
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 479 of file chthreads.c.
References chSysLock, and chThdExitS().
◆ chThdExitS()
| void chThdExitS | ( | msg_t | msg | ) |
Terminates the current thread.
The thread goes in the CH_STATE_FINAL state holding the specified exit status code, other threads can retrieve the exit status code by invoking the function chThdWait().
- Postcondition
- Exiting a non-static thread that does not have references (detached) causes the thread to remain in the registry. It can only be removed by performing a registry scan operation.
- Eventual code after this function will never be executed, this function never returns. The compiler has no way to know this so do not assume that the compiler would remove the dead code.
- Parameters
-
[in] msg thread exit code
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 503 of file chthreads.c.
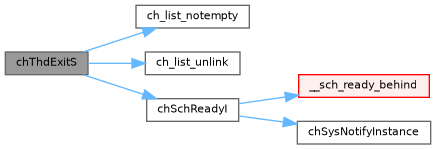
References CH_CFG_THREAD_EXIT_HOOK, CH_FLAG_MODE_MASK, CH_FLAG_MODE_STATIC, ch_list_notempty(), ch_list_unlink(), CH_STATE_FINAL, chDbgAssert, chSchGoSleepS, chSchReadyI(), chThdGetSelfX, ch_thread::exitcode, ch_thread::flags, ch_thread::refs, REG_REMOVE, threadref, ch_thread::u, unlikely, and ch_thread::waiting.
Referenced by chThdExit().
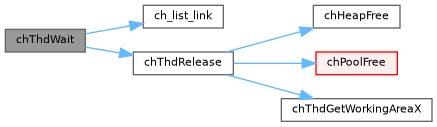
◆ chThdWait()
Blocks the execution of the invoking thread until the specified thread terminates then the exit code is returned.
This function waits for the specified thread to terminate then decrements its reference counter, if the counter reaches zero then the thread working area is returned to the proper allocator and the thread is removed from the registry.
- Precondition
- The configuration option
CH_CFG_USE_WAITEXITmust be enabled in order to use this function.
- Postcondition
- Enabling
chThdWait()requires 2-4 (depending on the architecture) extra bytes in thethread_tstructure.
- Note
- If
CH_CFG_USE_DYNAMICis not specified this function just waits for the thread termination, no memory allocators are involved.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The exit code from the terminated thread.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 560 of file chthreads.c.
References ch_list_link(), CH_STATE_FINAL, CH_STATE_WTEXIT, chDbgAssert, chDbgCheck, chSchGoSleepS, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdGetSelfX, chThdRelease(), ch_thread::exitcode, ch_thread::hdr, likely, ch_thread::list, ch_thread::refs, ch_thread::state, ch_thread::u, and ch_thread::waiting.
◆ chThdSetPriority()
Changes the running thread priority level then reschedules if necessary.
- Note
- The function returns the real thread priority regardless of the current priority that could be higher than the real priority because the priority inheritance mechanism.
- Parameters
-
[in] newprio the new priority level of the running thread
- Returns
- The old priority level.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 600 of file chthreads.c.
References chDbgCheck, chSchRescheduleS(), chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdGetSelfX, ch_thread::hdr, HIGHPRIO, ch_thread::pqueue, ch_priority_queue::prio, and ch_thread::realprio.

◆ chThdTerminate()
| void chThdTerminate | ( | thread_t * | tp | ) |
Requests a thread termination.
- Precondition
- The target thread must be written to invoke periodically
chThdShouldTerminate()and terminate cleanly if it returnstrue.
- Postcondition
- The specified thread will terminate after detecting the termination condition.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 636 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_FLAG_TERMINATE, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, and ch_thread::flags.
◆ chThdSleep()
| void chThdSleep | ( | sysinterval_t | time | ) |
Suspends the invoking thread for the specified time.
- Parameters
-
[in] time the delay in system ticks, the special values are handled as follow: - TIME_INFINITE the thread enters an infinite sleep state.
- TIME_IMMEDIATE this value is not allowed.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 655 of file chthreads.c.
References chSysLock, chSysUnlock, and chThdSleepS.
◆ chThdSleepUntil()
| void chThdSleepUntil | ( | systime_t | time | ) |
Suspends the invoking thread until the system time arrives to the specified value.
- Note
- The function has no concept of "past", all specifiable times are in the future, this means that if you call this function exceeding your calculated intervals then the function will return in a far future time, not immediately.
- See also
- chThdSleepUntilWindowed()
- Parameters
-
[in] time absolute system time
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 675 of file chthreads.c.
References chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdSleepS, chTimeDiffX, chVTGetSystemTimeX, and likely.
◆ chThdSleepUntilWindowed()
Suspends the invoking thread until the system time arrives to the specified value.
- Note
- The system time is assumed to be between
prevandnextelse the call is assumed to have been called outside the allowed time interval, in this case no sleep is performed.
- See also
- chThdSleepUntil()
- Parameters
-
[in] prev absolute system time of the previous deadline [in] next absolute system time of the next deadline
- Returns
- the
nextparameter
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 700 of file chthreads.c.
References chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdSleepS, chTimeDiffX, chTimeIsInRangeX(), chVTGetSystemTimeX, and likely.

◆ chThdYield()
| void chThdYield | ( | void | ) |
Yields the time slot.
Yields the CPU control to the next thread in the ready list with equal priority, if any.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 720 of file chthreads.c.
References chSchDoYieldS(), chSysLock, and chSysUnlock.

◆ chThdSuspendS()
| msg_t chThdSuspendS | ( | thread_reference_t * | trp | ) |
Sends the current thread sleeping and sets a reference variable.
- Note
- This function must reschedule, it can only be called from thread context.
- Parameters
-
[in] trp a pointer to a thread reference object
- Returns
- The wake up message.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 737 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_STATE_SUSPENDED, chDbgAssert, chSchGoSleepS, chThdGetSelfX, ch_thread::u, and ch_thread::wttrp.
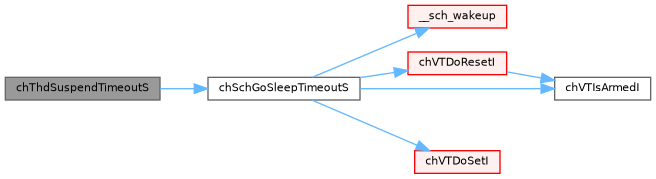
◆ chThdSuspendTimeoutS()
| msg_t chThdSuspendTimeoutS | ( | thread_reference_t * | trp, |
| sysinterval_t | timeout ) |
Sends the current thread sleeping and sets a reference variable.
- Note
- This function must reschedule, it can only be called from thread context.
- Parameters
-
[in] trp a pointer to a thread reference object [in] timeout the timeout in system ticks, the special values are handled as follow: - TIME_INFINITE the thread enters an infinite sleep state.
- TIME_IMMEDIATE the thread is not suspended and the function returns
MSG_TIMEOUTas if a timeout occurred.
- Returns
- The wake up message.
- Return values
-
MSG_TIMEOUT if the operation timed out.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 768 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_STATE_SUSPENDED, chDbgAssert, chSchGoSleepTimeoutS(), chThdGetSelfX, MSG_TIMEOUT, TIME_IMMEDIATE, ch_thread::u, unlikely, and ch_thread::wttrp.
Referenced by chPipeReadTimeout(), and chPipeWriteTimeout().
◆ chThdResumeI()
| void chThdResumeI | ( | thread_reference_t * | trp, |
| msg_t | msg ) |
Wakes up a thread waiting on a thread reference object.
- Note
- This function must not reschedule because it can be called from ISR context.
- Parameters
-
[in] trp a pointer to a thread reference object [in] msg the message code
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 793 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_STATE_SUSPENDED, chDbgAssert, chSchReadyI(), ch_thread::rdymsg, ch_thread::state, and ch_thread::u.
Referenced by chPipeReset().

◆ chThdResumeS()
| void chThdResumeS | ( | thread_reference_t * | trp, |
| msg_t | msg ) |
Wakes up a thread waiting on a thread reference object.
- Note
- This function must reschedule, it can only be called from thread context.
- Parameters
-
[in] trp a pointer to a thread reference object [in] msg the message code
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 816 of file chthreads.c.
References CH_STATE_SUSPENDED, chDbgAssert, chSchWakeupS, and ch_thread::state.
◆ chThdResume()
| void chThdResume | ( | thread_reference_t * | trp, |
| msg_t | msg ) |
Wakes up a thread waiting on a thread reference object.
- Note
- This function must reschedule, it can only be called from thread context.
- Parameters
-
[in] trp a pointer to a thread reference object [in] msg the message code
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 838 of file chthreads.c.
References chSysLock, chSysUnlock, and chThdResumeS.
Referenced by chPipeReadTimeout(), and chPipeWriteTimeout().
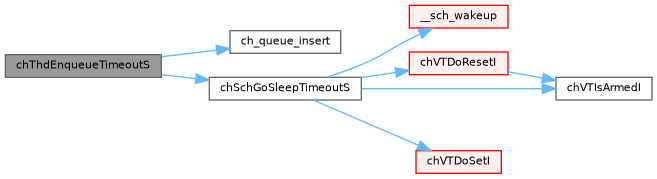
◆ chThdEnqueueTimeoutS()
| msg_t chThdEnqueueTimeoutS | ( | threads_queue_t * | tqp, |
| sysinterval_t | timeout ) |
Enqueues the caller thread on a threads queue object.
The caller thread is enqueued and put to sleep until it is dequeued or the specified timeouts expires.
- Parameters
-
[in] tqp pointer to a threads_queue_tobject[in] timeout the timeout in system ticks, the special values are handled as follow: - TIME_INFINITE the thread enters an infinite sleep state.
- TIME_IMMEDIATE the thread is not enqueued and the function returns
MSG_TIMEOUTas if a timeout occurred.
- Returns
- The message from
osalQueueWakeupOneI()orosalQueueWakeupAllI()functions.
- Return values
-
MSG_TIMEOUT if the thread has not been dequeued within the specified timeout or if the function has been invoked with TIME_IMMEDIATEas timeout specification.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 868 of file chthreads.c.
References ch_queue_insert(), CH_STATE_QUEUED, chSchGoSleepTimeoutS(), chThdGetSelfX, MSG_TIMEOUT, TIME_IMMEDIATE, and unlikely.
Referenced by chMBFetchTimeoutS(), chMBPostAheadTimeoutS(), and chMBPostTimeoutS().
◆ chThdDequeueNextI()
| void chThdDequeueNextI | ( | threads_queue_t * | tqp, |
| msg_t | msg ) |
Dequeues and wakes up one thread from the threads queue object, if any.
- Parameters
-
[in] tqp pointer to a threads_queue_tobject[in] msg the message code
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 889 of file chthreads.c.
References ch_queue_notempty(), and chThdDoDequeueNextI().
Referenced by chMBFetchI(), chMBFetchTimeoutS(), chMBPostAheadI(), chMBPostAheadTimeoutS(), chMBPostI(), and chMBPostTimeoutS().

◆ chThdDequeueAllI()
| void chThdDequeueAllI | ( | threads_queue_t * | tqp, |
| msg_t | msg ) |
Dequeues and wakes up all threads from the threads queue object.
- Parameters
-
[in] tqp pointer to a threads_queue_tobject[in] msg the message code
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 904 of file chthreads.c.
References ch_queue_notempty(), and chThdDoDequeueNextI().
Referenced by chMBResetI().

◆ chThdGetSelfX()
|
inlinestatic |
Returns a pointer to the current thread_t.
- Returns
- A pointer to the current thread.
- Function Class:
- This is an X-Class API, this function can be invoked from any context.
Definition at line 341 of file chthreads.h.
References __sch_get_currthread.
Referenced by chThdGetPriorityX(), and chThdShouldTerminateX().
◆ chThdGetPriorityX()
|
inlinestatic |
Returns the current thread priority.
- Note
- Can be invoked in any context.
- Returns
- The current thread priority.
- Function Class:
- This is an X-Class API, this function can be invoked from any context.
Definition at line 354 of file chthreads.h.
References chThdGetSelfX(), ch_thread::hdr, ch_thread::pqueue, and ch_priority_queue::prio.
◆ chThdGetTicksX()
Returns the number of ticks consumed by the specified thread.
- Note
- This function is only available when the
CH_DBG_THREADS_PROFILINGconfiguration option is enabled.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The number of consumed system ticks.
- Function Class:
- This is an X-Class API, this function can be invoked from any context.
Definition at line 370 of file chthreads.h.
References ch_thread::time.
◆ chThdGetWorkingAreaX()
|
inlinestatic |
Returns the working area base of the specified thread.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The working area base pointer.
- Function Class:
- This is an X-Class API, this function can be invoked from any context.
Definition at line 386 of file chthreads.h.
References ch_thread::wabase.
Referenced by chRegFindThreadByWorkingArea(), and chThdRelease().
◆ chThdTerminatedX()
|
inlinestatic |
Verifies if the specified thread is in the CH_STATE_FINAL state.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Return values
-
true thread terminated. false thread not terminated.
- Function Class:
- This is an X-Class API, this function can be invoked from any context.
Definition at line 401 of file chthreads.h.
References CH_STATE_FINAL, and ch_thread::state.
◆ chThdShouldTerminateX()
|
inlinestatic |
Verifies if the current thread has a termination request pending.
- Return values
-
true termination request pending. false termination request not pending.
- Function Class:
- This is an X-Class API, this function can be invoked from any context.
Definition at line 414 of file chthreads.h.
References CH_FLAG_TERMINATE, chThdGetSelfX(), and ch_thread::flags.

◆ chThdStartI()
Resumes a thread created with chThdCreateI().
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The pointer to the
thread_tstructure allocated for the thread into the working space area.
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 428 of file chthreads.h.
References CH_STATE_WTSTART, chDbgAssert, chSchReadyI(), and ch_thread::state.
◆ chThdSleepS()
|
inlinestatic |
Suspends the invoking thread for the specified number of ticks.
- Parameters
-
[in] ticks the delay in system ticks, the special values are handled as follow: - TIME_INFINITE the thread enters an infinite sleep state.
- TIME_IMMEDIATE this value is not allowed.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 447 of file chthreads.h.
References CH_STATE_SLEEPING, chDbgCheck, chSchGoSleepTimeoutS(), and TIME_IMMEDIATE.
◆ chThdQueueObjectInit()
|
inlinestatic |
Initializes a threads queue object.
- Parameters
-
[out] tqp pointer to the threads queue object
- Function Class:
- Object or module nitializer function.
Definition at line 461 of file chthreads.h.
References ch_queue_init().

◆ chThdQueueIsEmptyI()
|
inlinestatic |
Evaluates to true if the specified queue is empty.
- Parameters
-
[out] tqp pointer to the threads queue object
- Returns
- The queue status.
- Return values
-
false if the queue is not empty. true if the queue is empty.
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 476 of file chthreads.h.
References ch_queue_isempty(), and chDbgCheckClassI.
◆ chThdDoDequeueNextI()
|
inlinestatic |
Dequeues and wakes up one thread from the threads queue object.
Dequeues one thread from the queue without checking if the queue is empty.
- Precondition
- The queue must contain at least an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] tqp pointer to the threads queue object [in] msg the message code
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 494 of file chthreads.h.
References ch_queue_fifo_remove(), ch_queue_notempty(), CH_STATE_QUEUED, chDbgAssert, chSchReadyI(), ch_thread::rdymsg, ch_thread::state, threadref, and ch_thread::u.
Referenced by chThdDequeueAllI(), and chThdDequeueNextI().