Detailed Description
Synchronous inter-thread messages APIs and services.
Operation Mode
Synchronous messages are an easy to use and fast IPC mechanism, threads can both act as message servers and/or message clients, the mechanism allows data to be carried in both directions. Note that messages are not copied between the client and server threads but just a pointer passed so the exchange is very time efficient.
Messages are scalar data types of type msg_t that are guaranteed to be size compatible with data pointers. Note that on some architectures function pointers can be larger that msg_t.
Messages are usually processed in FIFO order but it is possible to process them in priority order by enabling the CH_CFG_USE_MESSAGES_PRIORITY option in chconf.h.
- Precondition
- In order to use the message APIs the
CH_CFG_USE_MESSAGESoption must be enabled inchconf.h.
- Postcondition
- Enabling messages requires 6-12 (depending on the architecture) extra bytes in the
thread_tstructure.

Macros | |
| #define | __ch_msg_insert(qp, tp) |
Functions | |
| msg_t | chMsgSend (thread_t *tp, msg_t msg) |
| Sends a message to the specified thread. | |
| thread_t * | chMsgWaitS (void) |
| Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message. | |
| thread_t * | chMsgWaitTimeoutS (sysinterval_t timeout) |
| Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message or a timeout to occur. | |
| thread_t * | chMsgPollS (void) |
| Poll to check for an incoming message. | |
| void | chMsgRelease (thread_t *tp, msg_t msg) |
| Releases a sender thread specifying a response message. | |
| static thread_t * | chMsgWait (void) |
| Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message. | |
| static thread_t * | chMsgWaitTimeout (sysinterval_t timeout) |
| Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message or a timeout to occur. | |
| static thread_t * | chMsgPoll (void) |
| Poll to check for an incoming message. | |
| static bool | chMsgIsPendingI (thread_t *tp) |
Evaluates to true if the thread has pending messages. | |
| static msg_t | chMsgGet (thread_t *tp) |
| Returns the message carried by the specified thread. | |
| static void | chMsgReleaseS (thread_t *tp, msg_t msg) |
| Releases the thread waiting on top of the messages queue. | |
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ __ch_msg_insert
| #define __ch_msg_insert | ( | qp, | |
| tp ) |
Definition at line 54 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
Referenced by chMsgSend().
Function Documentation
◆ chMsgSend()
Sends a message to the specified thread.
The sender is stopped until the receiver executes a chMsgRelease()after receiving the message.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp the pointer to the thread [in] msg the message
- Returns
- The answer message from
chMsgRelease().
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 81 of file rt/src/chmsg.c.
References __ch_msg_insert, CH_STATE_SNDMSGQ, CH_STATE_WTMSG, chDbgCheck, chSchGoSleepS, chSchReadyI(), chSysLock, chSysUnlock, chThdGetSelfX, ch_thread::msgqueue, ch_thread::rdymsg, ch_thread::sentmsg, ch_thread::state, and ch_thread::u.
Referenced by chDelegateCallVeneer().

◆ chMsgWaitS()
| thread_t * chMsgWaitS | ( | void | ) |
Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message.
- Postcondition
- After receiving a message the function
chMsgGet()must be called in order to retrieve the message and thenchMsgRelease()must be invoked in order to acknowledge the reception and send the answer.
- Note
- If the message is a pointer then you can assume that the data pointed by the message is stable until you invoke
chMsgRelease()because the sending thread is suspended until then. - The reference counter of the sender thread is not increased, the returned pointer is a temporary reference.
- Returns
- A pointer to the thread carrying the message.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 115 of file rt/src/chmsg.c.
References ch_queue_fifo_remove(), CH_STATE_SNDMSG, CH_STATE_WTMSG, chDbgCheckClassS, chMsgIsPendingI(), chSchGoSleepS, chThdGetSelfX, ch_thread::msgqueue, ch_thread::state, and threadref.

◆ chMsgWaitTimeoutS()
| thread_t * chMsgWaitTimeoutS | ( | sysinterval_t | timeout | ) |
Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message or a timeout to occur.
- Postcondition
- After receiving a message the function
chMsgGet()must be called in order to retrieve the message and thenchMsgRelease()must be invoked in order to acknowledge the reception and send the answer.
- Note
- If the message is a pointer then you can assume that the data pointed by the message is stable until you invoke
chMsgRelease()because the sending thread is suspended until then. - The reference counter of the sender thread is not increased, the returned pointer is a temporary reference.
- Parameters
-
[in] timeout the number of ticks before the operation timeouts, the following special values are allowed: - TIME_INFINITE no timeout.
- Returns
- A pointer to the thread carrying the message.
- Return values
-
NULL if a timeout occurred.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 152 of file rt/src/chmsg.c.
References ch_queue_fifo_remove(), CH_STATE_SNDMSG, CH_STATE_WTMSG, chDbgCheckClassS, chMsgIsPendingI(), chSchGoSleepTimeoutS(), chThdGetSelfX, MSG_OK, ch_thread::msgqueue, ch_thread::state, and threadref.
Referenced by chMsgWaitTimeout().

◆ chMsgPollS()
| thread_t * chMsgPollS | ( | void | ) |
Poll to check for an incoming message.
- Postcondition
- If a message is available the function
chMsgGet()must be called in order to retrieve the message and thenchMsgRelease()must be invoked in order to acknowledge the reception and send the answer.
- Note
- If the message is a pointer then you can assume that the data pointed by the message is stable until you invoke
chMsgRelease()because the sending thread is suspended until then. - The reference counter of the sender thread is not increased, the returned pointer is a temporary reference.
- Returns
- Result of the poll.
- Return values
-
NULL if no incoming message waiting.
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 186 of file rt/src/chmsg.c.
References ch_queue_fifo_remove(), CH_STATE_SNDMSG, chMsgIsPendingI(), chThdGetSelfX, ch_thread::msgqueue, ch_thread::state, and threadref.
Referenced by chMsgPoll().

◆ chMsgRelease()
Releases a sender thread specifying a response message.
- Precondition
- Invoke this function only after a message has been received using
chMsgWait().
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread [in] msg message to be returned to the sender
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 208 of file rt/src/chmsg.c.
References CH_STATE_SNDMSG, chDbgAssert, chMsgReleaseS, chSysLock, chSysUnlock, and ch_thread::state.
Referenced by chDelegateDispatch(), and chDelegateDispatchTimeout().
◆ chMsgWait()
|
inlinestatic |
Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message.
- Postcondition
- After receiving a message the function
chMsgGet()must be called in order to retrieve the message and thenchMsgRelease()must be invoked in order to acknowledge the reception and send the answer.
- Note
- If the message is a pointer then you can assume that the data pointed by the message is stable until you invoke
chMsgRelease()because the sending thread is suspended until then. - The reference counter of the sender thread is not increased, the returned pointer is a temporary reference.
- Returns
- A pointer to the thread carrying the message.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 95 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
References chMsgWaitS, chSysLock, and chSysUnlock.
Referenced by chDelegateDispatch().
◆ chMsgWaitTimeout()
|
inlinestatic |
Suspends the thread and waits for an incoming message or a timeout to occur.
- Postcondition
- After receiving a message the function
chMsgGet()must be called in order to retrieve the message and thenchMsgRelease()must be invoked in order to acknowledge the reception and send the answer.
- Note
- If the message is a pointer then you can assume that the data pointed by the message is stable until you invoke
chMsgRelease()because the sending thread is suspended until then. - The reference counter of the sender thread is not increased, the returned pointer is a temporary reference.
- Parameters
-
[in] timeout the number of ticks before the operation timeouts, the following special values are allowed: - TIME_IMMEDIATE immediate timeout.
- TIME_INFINITE no timeout.
- Returns
- A pointer to the thread carrying the message.
- Return values
-
NULL if a timeout occurred.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 128 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
References chMsgWaitTimeoutS(), chSysLock, and chSysUnlock.
Referenced by chDelegateDispatchTimeout().
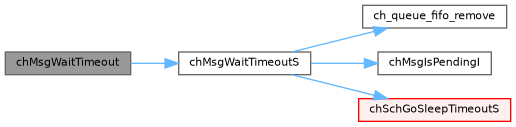
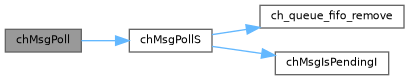
◆ chMsgPoll()
|
inlinestatic |
Poll to check for an incoming message.
- Postcondition
- If a message is available the function
chMsgGet()must be called in order to retrieve the message and thenchMsgRelease()must be invoked in order to acknowledge the reception and send the answer.
- Note
- If the message is a pointer then you can assume that the data pointed by the message is stable until you invoke
chMsgRelease()because the sending thread is suspended until then. - The reference counter of the sender thread is not increased, the returned pointer is a temporary reference.
- Returns
- A pointer to the thread carrying the message.
- Return values
-
NULL if no incoming message waiting.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 155 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
References chMsgPollS(), chSysLock, and chSysUnlock.
◆ chMsgIsPendingI()
|
inlinestatic |
Evaluates to true if the thread has pending messages.
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The pending messages status.
- Function Class:
- This is an I-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by both threads and interrupt handlers.
Definition at line 173 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
References chDbgCheckClassI, ch_thread::msgqueue, and ch_queue::next.
Referenced by chMsgPollS(), chMsgWaitS(), and chMsgWaitTimeoutS().
◆ chMsgGet()
Returns the message carried by the specified thread.
- Precondition
- This function must be invoked immediately after exiting a call to
chMsgWait().
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread
- Returns
- The message carried by the sender.
- Function Class:
- Normal API, this function can be invoked by regular system threads but not from within a lock zone.
Definition at line 190 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
References CH_STATE_SNDMSG, chDbgAssert, ch_thread::sentmsg, ch_thread::state, and ch_thread::u.
◆ chMsgReleaseS()
Releases the thread waiting on top of the messages queue.
- Precondition
- Invoke this function only after a message has been received using
chMsgWait().
- Parameters
-
[in] tp pointer to the thread [in] msg message to be returned to the sender
- Function Class:
- This is an S-Class API, this function can be invoked from within a system lock zone by threads only.
Definition at line 207 of file rt/include/chmsg.h.
References chDbgCheckClassS, and chSchWakeupS.